| Patent Search Tool | PatentCloud |
| Search Date | Sep. 8, 2022 |
| Search scope and Results |  |

Fig. 1 Major patent owners of blockchain x future cars related patents
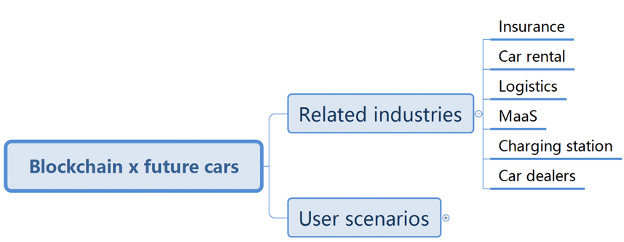
Fig.2 Related industries of blockchain x future cars patents
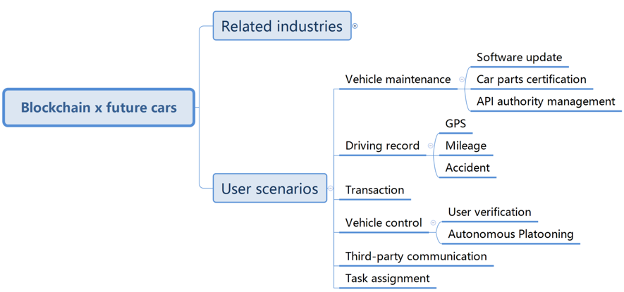
Fig.3 User scenarios involved in blockchain x future cars patents
With respect to vehicle maintenance applications, blockchain technologies may be used in software updating, car parts certification and API authority management. Software updating relates to the use of blockchain technologies to share information such as updating among servers, for instance map updating information. Car parts certification requires the use of blockchain to determine whether a car part has been authorized to be installed. API authority management involves the use of blockchain to determine API access rules. Let us take Volvo’s patent US20200388091 (Secure installation of approved parts using blockchain) as an example, as shown in Fig.4. The patent highlights the use of blockchain to store information related to approved parts and their operation parameters. When replacing new parts, the operation parameters of the new parts are compared to those of approved parts to determine whether the new parts have been approved. Therefore, the installment of unapproved parts may be avoided.
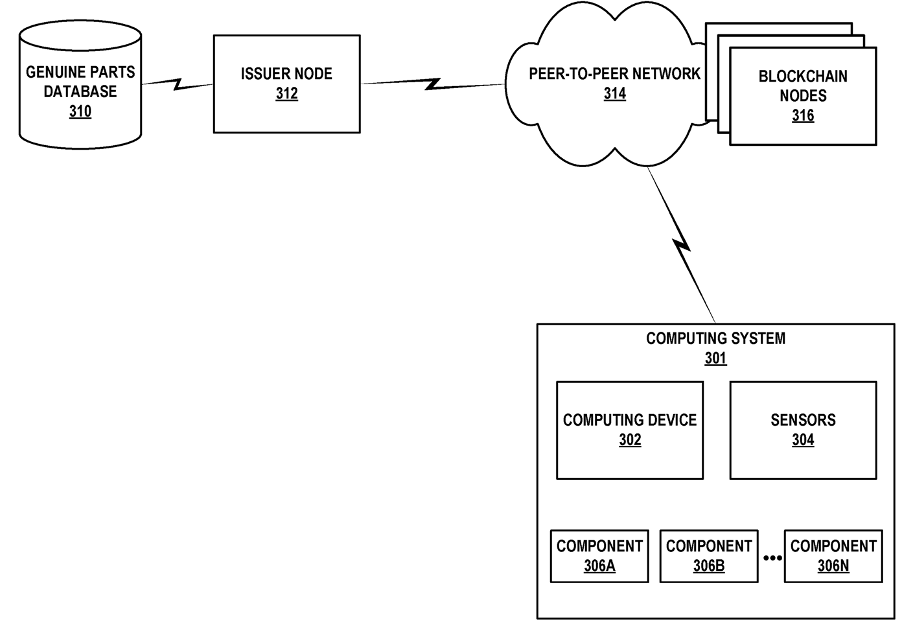
Fig.4 Drawing of Volvo’s patent US20200388091
In driving record applications, various driving information can be recorded in a blockchain, including GPS records, mileage records and accident records. Taking Walmart’s patent US10627250 (System and method for tracking vehicle mileage using blockchain) as an example, as shown in Fig.5, the patent relates to logistics management system. When a vehicle uses a route previously followed, the system will identify a previous block that recorded the previous travel data, and form a reference block of the difference between the current travel data and the previous one (such as different departure time). The reference block is added to the previous block as a side block, as shown in Fig.6. Therefore, the system can quickly retrieve required driving records to enhance management efficiency.
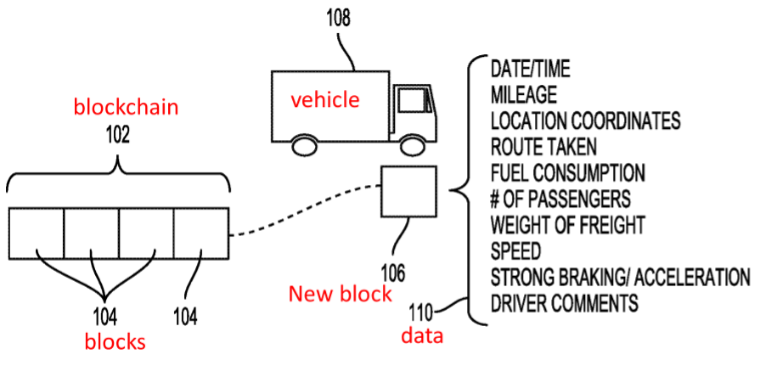
Fig.5 Drawing of Walmart’s patent US10627250
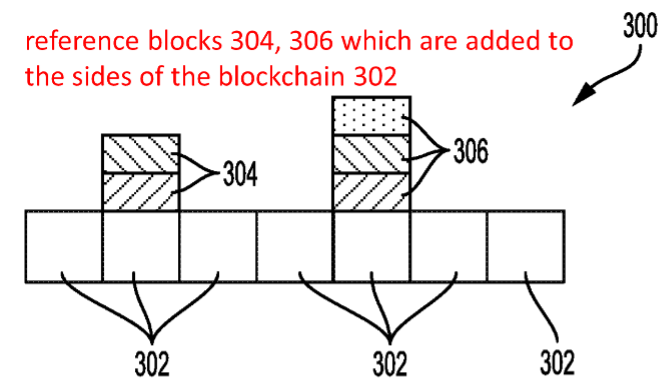
Fig.6 Drawing of Walmart’s patent US10627250
The most mentioned user scenario of blockchain x future cars are vehicle related transactions, such as toll payment or charging billing. An issue with the existing techniques is the lack of authentication scheme for the EV to allow guest charging using a smart sub metering mechanism at home or commercial complex. Further, an EV with a single authentication key may not be able to charge the rechargeable batteries associated with the EV from multiple energy distribution vendors, home or commercial complex. Let us take ABB’s patent US20220227251 (A method and system for charging electric vehicles (EVs) using block chain) as an example, as shown in Fig.7. The patent uses an EV system operator 105 to determine sister blockchains (401, 402, 403) associated with multiple energy distribution vendors (104A,104B, 104C) for storing energy transactions. EV system operator no. 105 stores all the energy transactions associated with energy distribution vendor no. 104 in a mother block chain. In such way, the authentication data of all vendors can be recorded, and the charging service of all vendors can be managed.
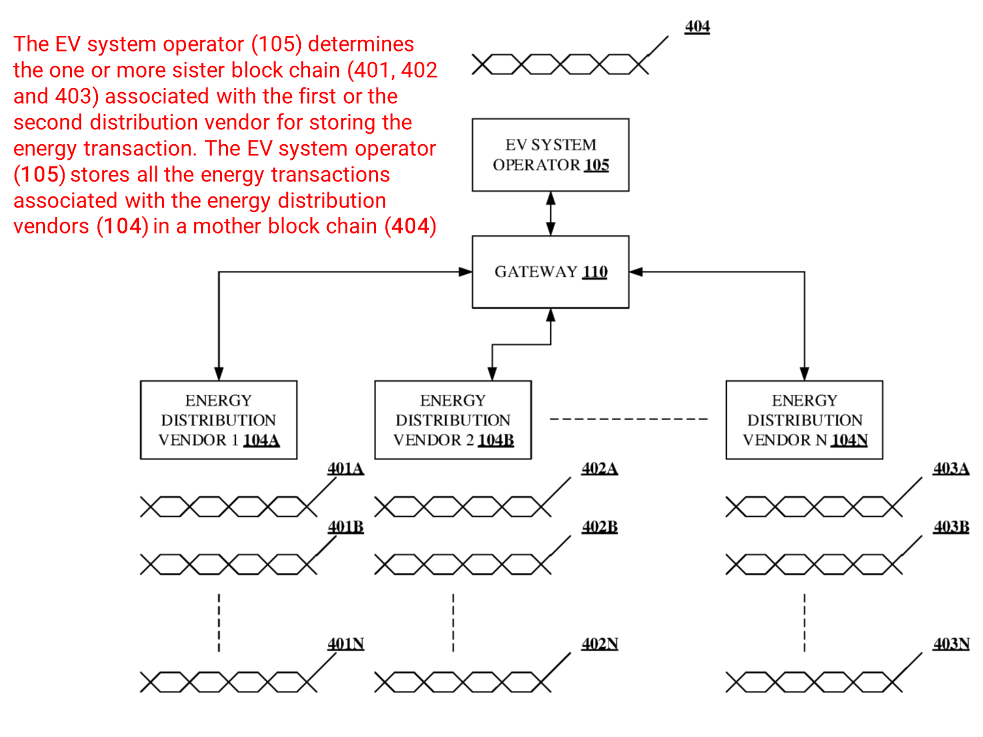
Fig.7 Drawing of ABB’s patent US20220227251
Blockchain technologies can be used in vehicle control such as user verification and autonomous platooning. Let us take LG’s patent US11402853 (Method for controlling platooning and autonomous vehicle based on blockchain) as an example, as shown in Fig.8. The patent uses blockchain to manage data transmission among platooning vehicles and detect external hacking. When a slave vehicle is hacked, the leader vehicle will rearrange the position of the hacked slave vehicle in the platooning or disengage the vehicle.
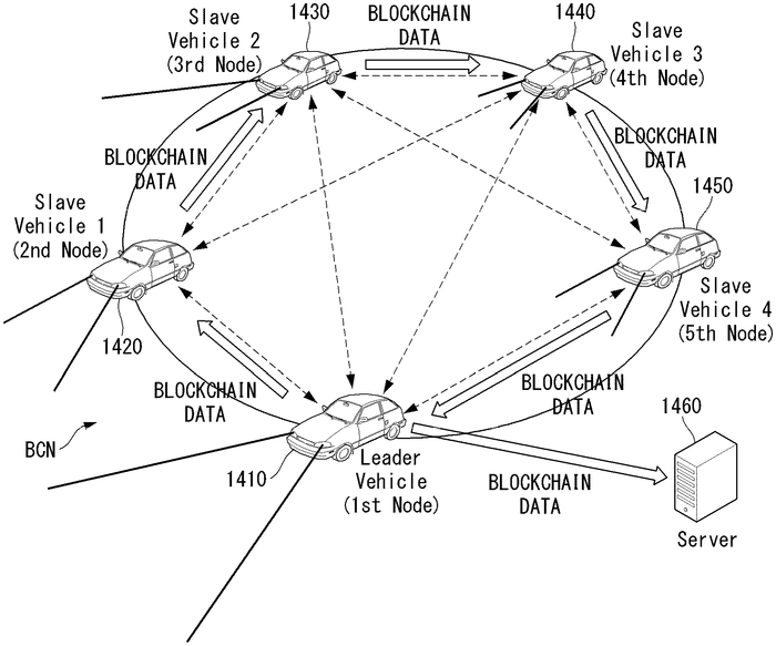
Fig.8 Drawing of LG’s US11402853
Taking GM’s patent US10783600 (Method and system using a blockchain database for data exchange between vehicles and entities) as an example, the patent provides a method of using blockchain to exchange data between autonomous vehicles and other entities, as shown in Fig.9. The method includes executing blockchain agreements between the entities participating in a blockchain exchange for distributing event information related to the vehicle operation. The blockchain exchange includes a plurality of databases having blockchains of data blocks for storing the event information. A particular entity among the entities generates the event information related to vehicle operation, and event information is validated the by a consensus of the entities. Then, upon validating by the consensus, a blockchain is appended within the blockchain database for enabling each entity to have access to a same replicated block data with the event information to enable enhanced vehicle operations of multiple vehicles based on the same replicated block data.
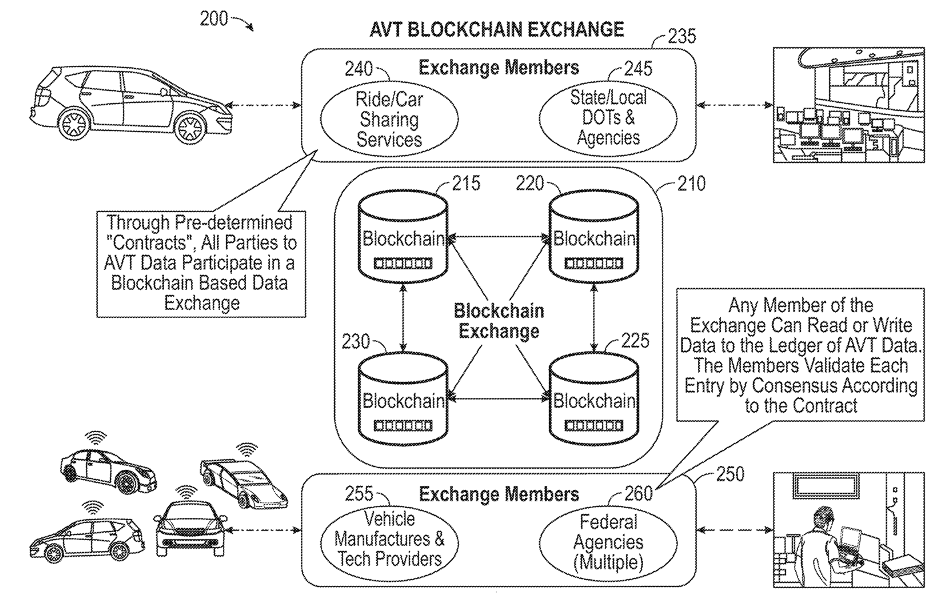
Fig.9 Drawing of GM’s patent US10783600
Taking IBM’s patent US20190378418 (Performing vehicle logistics in a blockchain) as an example, as shown in Fig.10, the patent highlights the use of blockchain technologies to manage logistic tasks and platooning vehicles. When a vehicle receives a task, a blockchain (130) determines whether the task of the vehicle (such as vehicle type, loading or destination) that meets the criteria of a platoon according to a smart contract. Once met, vehicles in the platoon can vote to decide whether the new vehicle can join the platoon. In such way, various logistic tasks can be quickly integrated into platoon and therefore reduce energy consumption.
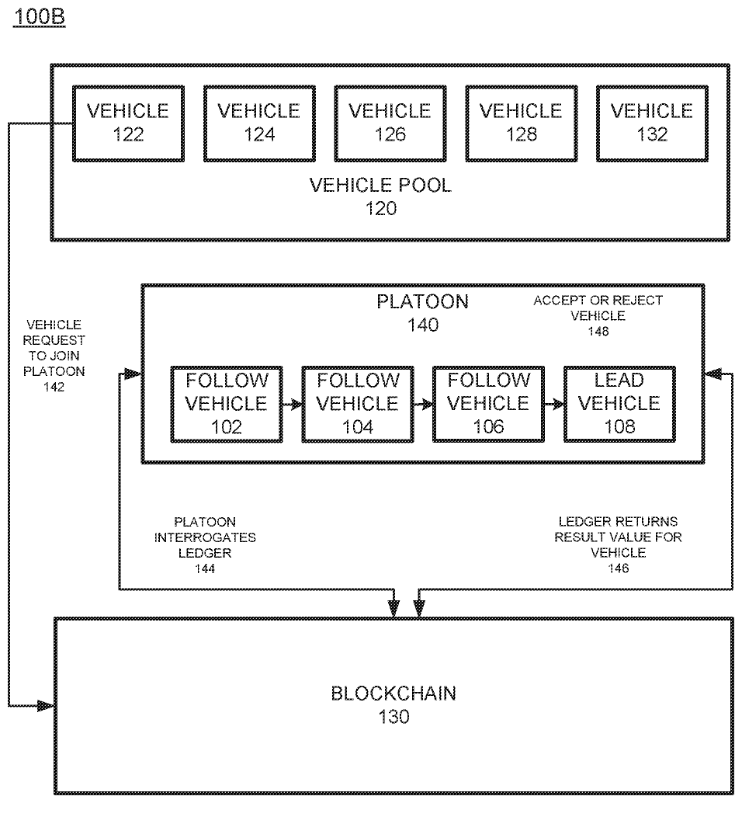
Fig.10 Drawing of IBM’s patent US20190378418
 |
By Jean Chou, Taiwan Patent Attorney / Certified Valuation Analyst at WISPRO Technology Consulting Corporation Email: jeanchou@wispro.com |
![[Expert Views] How Tesla Explores its Patent Assets](https://demo2.mih-ev.org/s3/mih%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2023%2F01%2FWispro-Expert-Views.png)
Wispro
2023-05-26

MIH Consortium
2023-03-20

MIH Consortium
2023-02-22